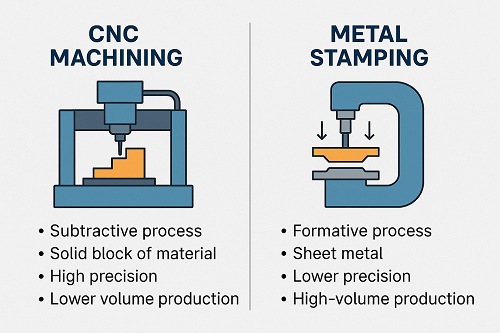
CNC machining is a precise, computer-controlled manufacturing process that removes material from a solid block (called a billet or workpiece) using cutting tools. Machines like lathes, mills, and routers are guided by a programmed code (G-code), which defines tool paths, speed, and depth.
Metal stamping is a high-speed forming process that uses a punch and die to shape flat metal sheets into desired parts. It's usually done with a hydraulic or mechanical press and is suitable for mass production.
| Category | CNC Machining | Metal Stamping |
| Process Type | Subtractive (removes material) | Formative (shapes material with force) |
| Material Used | Solid blocks or rods (billets) | Flat sheet metal |
| Precision | Very high (up to ±0.001") | Moderate to high, depends on tooling |
| Tooling Cost | Low to medium | High (custom dies are expensive) |
| Per-Unit Cost | High for large volumes | Very low for large volumes |
| Setup Time | Short (after programming) | Long (tooling and die creation takes time) |
| Best For | Prototypes, low-volume, complex shapes | Mass production of simple to moderately complex parts |
| Design Flexibility | Very high (easy to change code) | Low (changing dies is expensive and time-consuming) |
| Speed | Slower than stamping | Very fast for large batches |
| Material Waste | Higher (material is cut away) | Lower (more efficient use of sheet metal) |
| Surface Finish | Excellent, depending on tooling and process | May require secondary operations (deburring, finishing) |
You require parts with excellent surface finish or internal features (e.g., threaded holes).
You’re working in industries like automotive, electronics, or appliances, where millions of identical parts are needed.
| Industry | CNC Machining Examples | Metal Stamping Examples |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, brackets, structural parts | Light housings, clips |
| Automotive | Engine components, gear housings | Body panels, seat brackets, battery enclosures |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments, implants | Disposable cases, shields |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, custom enclosures | Connectors, mounting plates |
| Prototyping | One-off or iterative design parts | Rarely used unless testing stamping tools |
If you're making a few complex parts, go with CNC.
If you're making millions of identical sheet metal parts, choose stamping.